AAA weekly
2020-04-20
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Shinry Technologies: Strengthens Production, R&D to Meet Rising Demand
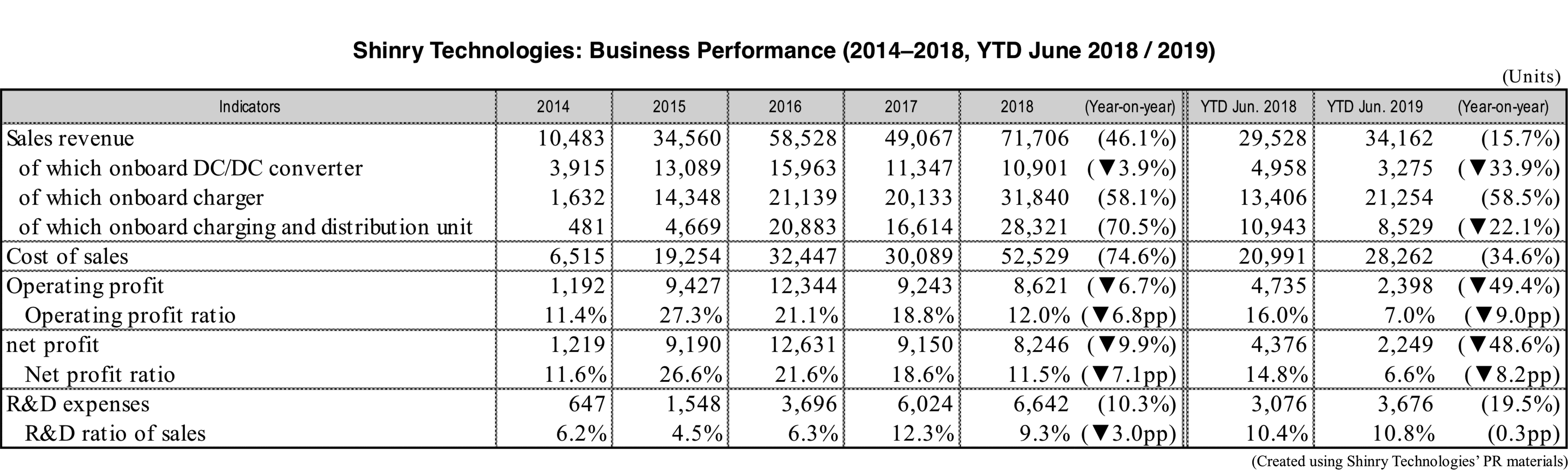
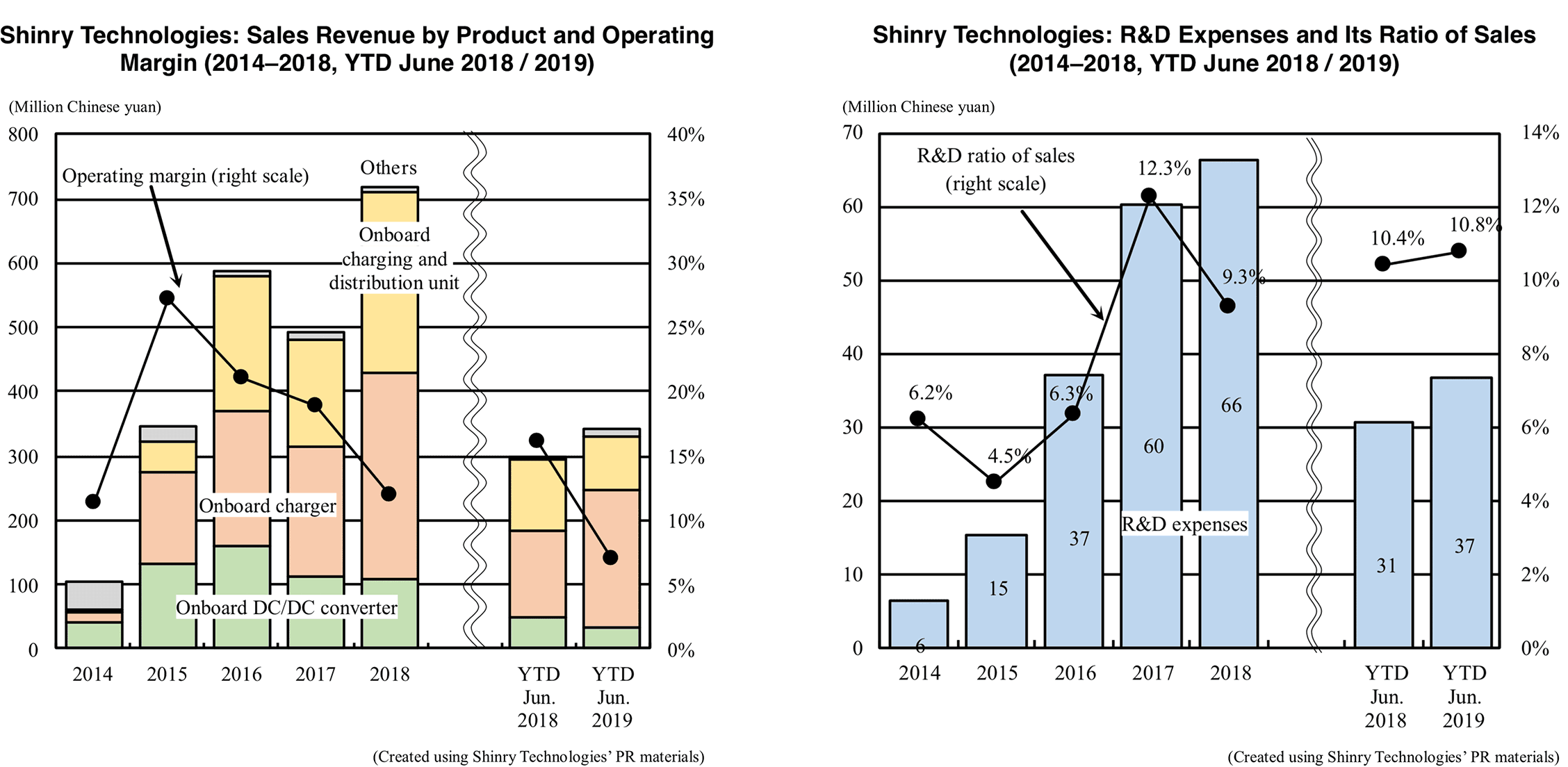
Shinry Technologies is a component supplier that manufactures onboard chargers, DC/DC converters and high-power chargers for energy-saving and new-energy vehicles. Sales in the first six months of 2019 grew 15.7% year-on-year to 310 million Chinese yuan, driven by the growth of the new-energy vehicle (NEV) market. Amid the reduction of NEV purchase subsidies, automakers have lowered procurement cost. As a result, Shinry’s operating profit declined 49.4% to 23.98 million CNY, operating profit margin dropping to a record low of 7.0%. In response to intensifying competition in the NEV market, Shinry has begun to reduce costs, while it also announced a policy to expand its supply scale, reduce selling prices and promote technological innovation between 2019 and 2021.
Shinry Technologies: Company Overview and Milestones (As of March 2020)
Company Overview
| Company name: | Shinry Technologies Co., Ltd. |
| Location: | Shenzhen, Guangdong province |
| Established: | January 2005 |
| Stock listing: | Since May 2018 on Shenzhen Stock Exchange (stock code: 300745) |
| Chairman: | Wu Renhua |
| Capital: | 114.51 Chinese yuan |
| Ownership: | Wu Renhua (individual) 30.79%, Peng Shengwen 5.35%, Shenzhen Jisitai Technology 4.84%, Tang Dongyuan 4.6%, Fortune Capital 3.36%, etc. (as of March 2020) |
| Employees: | Over 1,200 people (as of October 2019) |
| Main products: | Power supply solutions for NEVs (onboard DC/DC converter, onboard charger, etc.) |
| Customers: | BAIC BJEV, Changan Automobile, Jianghuai Automobile, Golden Dragon Bus and other automakers, Shenzhen Inovance Technology, Shenzhen V&T Technologies, Beijing Yinaite Technology, Jee Automation Equipment, etc. Subsidiaries: Jiangsu Shinry New Energy Technology, Hangzhou Shinry Technology, Shanghai Shinry Electronic Control Technology, Shiyan Branch Office, Bao’an Branch Office. |
Milestones
| 2005: | Founded in Shenzhen. |
| 2006: | Began R&D development of DC/DC converters |
| 2007: | Acquired ISO9001 quality management system certification. DC/DC converter passed road test. |
| 2008: | Began supply of Changan Automobile’s HEV taxis. |
| 2009: | Recognized as a China Hi-tech Enterprise |
| 2010: | Began development of onboard chargers. First plant went into operation. |
| 2011: | Launched a DC/DC converter development project. Shinry’s DC/DC converters were used for large buses serving during the 2011 Summer Universiade in Shenzhen, Guangdong province, China. |
| 2012: | Acquired TS16949 quality management system certification. Second plant went into operation with a monthly production capacity of 5,000 units. |
| 2014: | Hangzhou Shinry Technology was established. |
| 2015: | Became an onboard power supply manufacturer. Renewed production facilities. |
| 2016: | Shanghai Shinry Electronic Control Technology was established. Introduced PLM and MES systems. Acquired ISO14001 environmental management system certification. |
| 2017: | The R&D headquarters went into operation. Lingya plant went into operation. Acquired IATF16949 quality management system certification. |
| 2018: | Went public on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. |
| 2019: | The test center was certified by CNAS. |
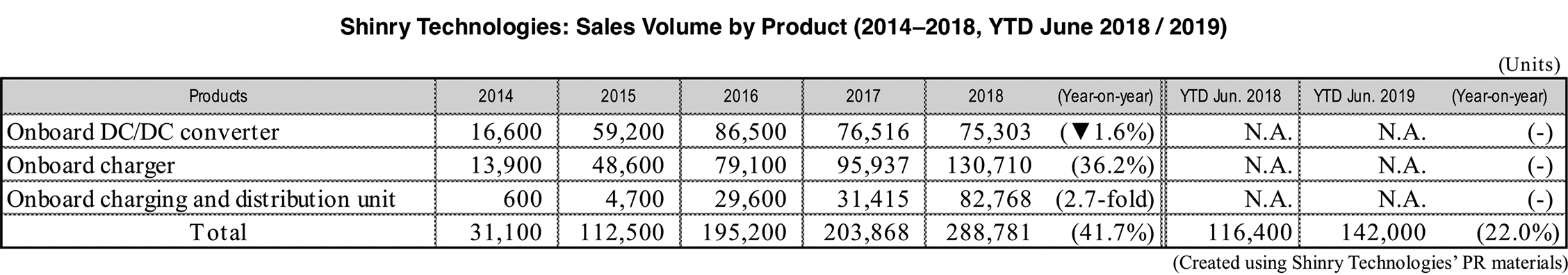
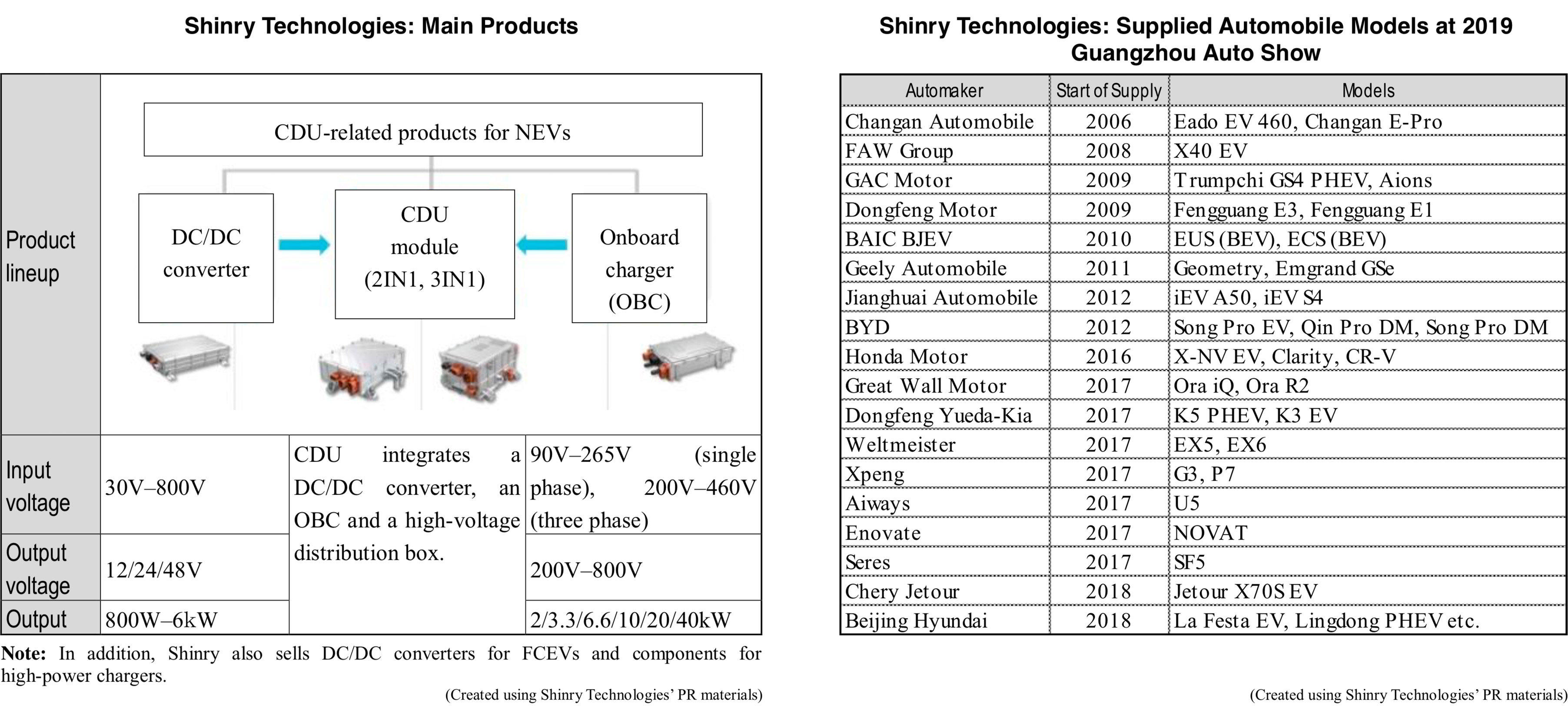
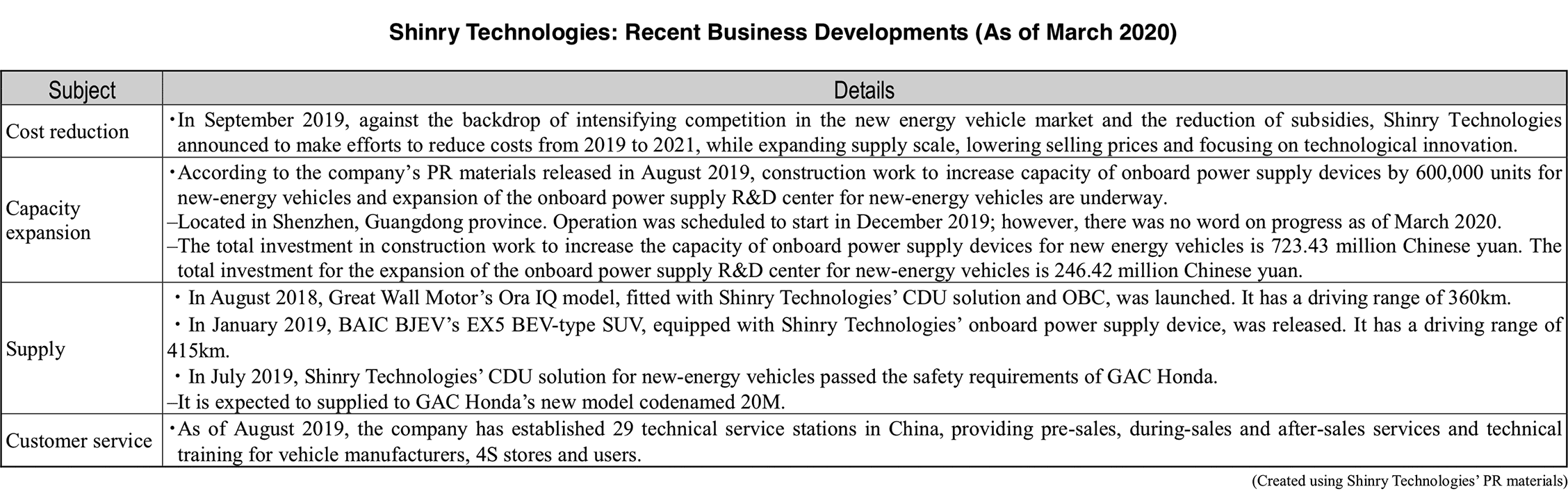
Shinry entered the manufacturing and sales business of power supply systems for NEVs in 2006 and has been focusing on expanding its customer base. Nearly 40 vehicle models exhibited at the Guangzhou auto show in November 2019 were equipped with Shinry’s products (company announcement). Looking at the company’s recent supply history, Shinry supplied Great Wall Motor supplied CDU solutions and G5 OBC to the Ora IQ model which was launched in August 2018. BAIC BJEV’s EX5 BEV-type SUV, equipped with Shinry’s onboard power supply device, was released in January 2019. In addition, Shinry’s CDU solution for new-energy vehicles passed the safety requirements of GAC Honda in July 2019.
Regarding production capacity expansion, according to the company’s PR materials released in August 2019, Shinry has invested over 700 million Chinese yuan in construction work to increase capacity of onboard power supply devices by 600,000 units for new-energy vehicles.
The company is also focusing on investing in R&D and strengthening its related facilities. R&D expenses in the first six months of 2019 were 36.76 million Chinese yuan, going up 19.5%. R&D expenses have been exceeding 8.0% since 2018. Moreover, the company’s on-board power supply R&D center has been expanded and is expected to start operation in 2020.