AAA weekly
2019-09-24
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Honda: eMaaS that Integrates Energy Business, Mobility
In July 2019, Honda Motor held a press meeting (Honda Meeting 2019) to discuss the future direction of technology development toward the fulfillment of the company’s 2030 Vision, which is “to serve people worldwide with the joy of expanding their life’s potential.” Presentations were made on specific frameworks such as eMaaS and next-generation mobility / digital solutions for realizing a carbon-neutral society and a zero-accident society. Honda's CASE is a combination of Connected, Autonomous, Services, and Electrification plus its driving force which is energy. As an automobile manufacturer that also handles the energy business, eMaaS, which combines mobility services (MaaS) and energy services (EaaS), is the foundation of next-generation services. eMaaS is in common with Honda's philosophy of “creating energy, consuming energy, and connecting with energy” advocated during the company’s FCEV strategy. In order to realize a carbon-neutral society, it is not enough to expand the use of electric vehicles. A carbon-free society can only be realized by supplying renewable energy to BEVs (electricity), FCEVs (hydrogen) and ICEVs (fuel), and expanding the range of use. Honda clearly indicated in its announcement that synthetic fuel (e-fuel) made with electricity derived from renewable energy will be the key particularly for conventional vehicles.
eMaaS
Honda is actively promoting business alliances in Japan and overseas to promote EaaS. In Europe, Honda has partnered with relevant companies to carry out technology demonstration regarding energy management solutions, and in Indonesia, Honda is conducting demonstration experiments on battery sharing for electric motorcycles. In addition, Suzuki, Yamaha Motor and Kawasaki Heavy Industries announced in April 2019 that they would establish a consortium on exchangeable batteries for electric motorcycles in Japan.
Honda Motor: Outline of Overall Business Strategy – Aiming for Carbon-free Society Using Well to Wheel Analysis
Outline of eMaaS
・Honda advocates CASE+e because the automaker thinks that energy is the driving force which is necessary to realize CASE. As an automobile manufacturer which is also involved in the energy business, Honda is aiming to provide a well-to-wheel total seamless service centered on eMaaS. eMaas is a combination of Energy as a Service (EaaS) and Mobility as a Service (MaaS). –The strategy is based on the dissemination of energy, which is the driving force of electric vehicles, not the diffusion of electric vehicles, due to the problems of charging and filling infrastructure, installation costs, and battery costs. – Honda's CASE is Connected, Autonomous, Services, Electrification (+ energy). ・Honda is working on energy management solutions to accelerate the realization of eMaaS. In March 2019, the company invested in Germany’s Ubitricity, which develops solutions for street charging in urban areas, and UK’s Moixa, a home battery storage company. In Europe, V1G (vehicle-to-grid unidirectional power flow) / V2G (vehicle-to-grid bidirectional power flow) are in the demonstration phase. – Technology demonstration is planned to be carried out in cooperation with Ubitricity using Smart Cable (AC charger) in London, UK and Offenbach, Germany.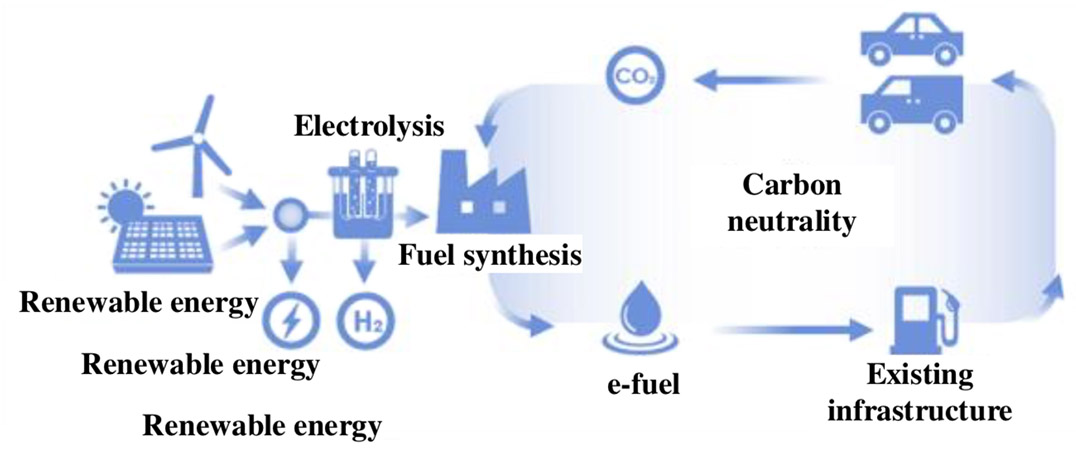 – Honda formed a partnership with Moixa in the areas of charge / discharge management and capacity management of BEV drive batteries.
・Honda, whose goal is carbon neutrality, envisions a scenario that supports a multi-pathway society that combines an electric mobility society based on the electrification of mobility and a renewable fuel society which is needed for the operation of electric mobility.
– Electric mobility society: Responds to user convenience issues taking into account regional characteristics, infrastructure conditions and applications among other aspects using various services such as smart chargers, stationary and portable distributed power generation, battery storage stations, and removable portable batteries.
– Renewable fuel society: Expands renewable energy producing enough electricity, hydrogen and other energy sources that meet demand.
– Honda formed a partnership with Moixa in the areas of charge / discharge management and capacity management of BEV drive batteries.
・Honda, whose goal is carbon neutrality, envisions a scenario that supports a multi-pathway society that combines an electric mobility society based on the electrification of mobility and a renewable fuel society which is needed for the operation of electric mobility.
– Electric mobility society: Responds to user convenience issues taking into account regional characteristics, infrastructure conditions and applications among other aspects using various services such as smart chargers, stationary and portable distributed power generation, battery storage stations, and removable portable batteries.
– Renewable fuel society: Expands renewable energy producing enough electricity, hydrogen and other energy sources that meet demand.”Create-connect-consume” philosophy
・Honda’s FCEV philosophy of “creating energy, consuming energy, and connecting with energy” is applied to the entire electrification process. It was launched as eMaaS. Honda envisions a carbon-neutral society where electricity is generated from renewable energy, electric power is used for electric mobility, and movement is achieved by electric mobility.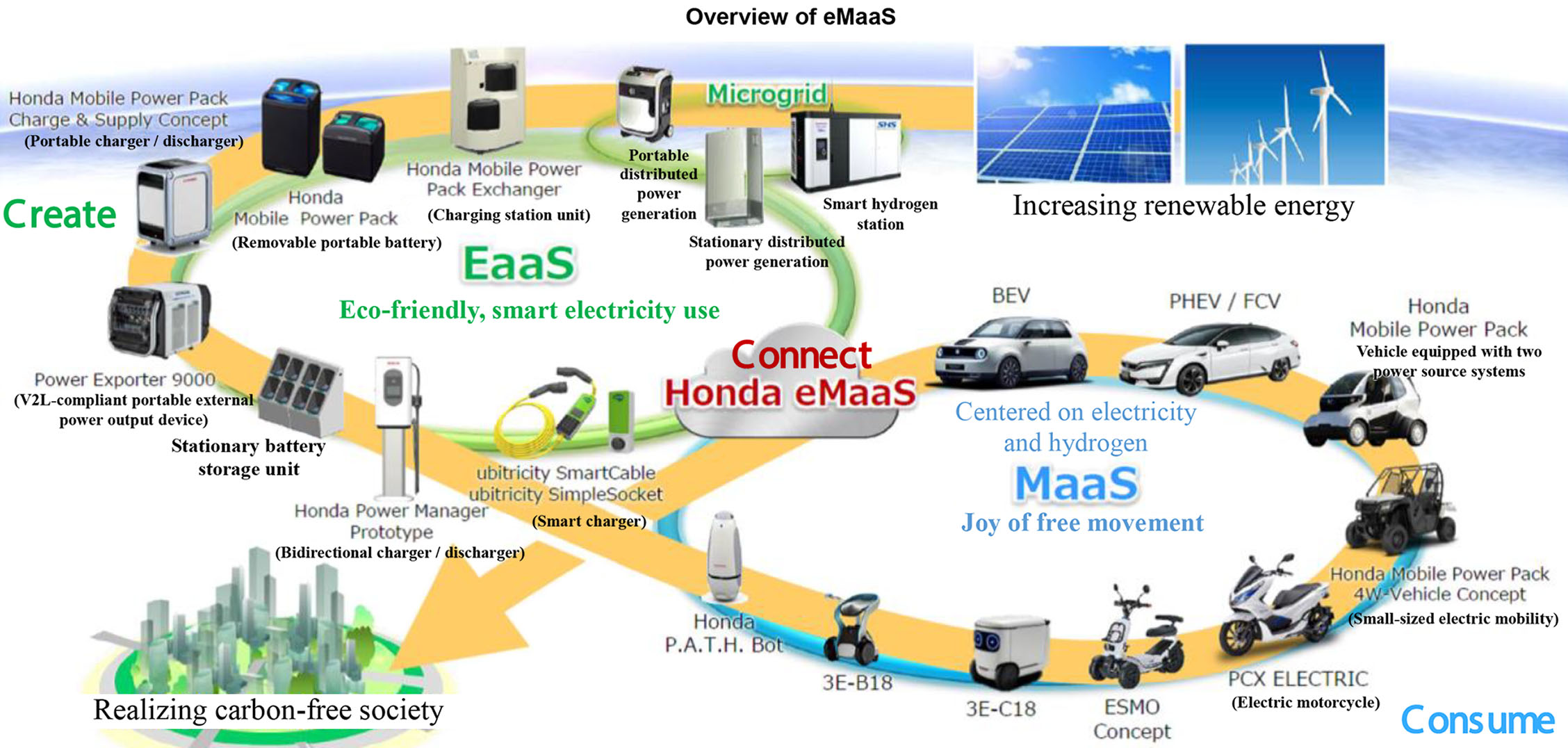
Honda Motor: Vehicle Strategy by Sector
Four-wheeler sector
・The four-wheeler sector puts emphasis on a carbon neutral society and zero-accident society. As a vision for 2030, Honda will promote electrification based on PHEV, and raise the share of electric vehicles in global sales to two-thirds by 2030. ・Honda recommends to realize carbon-free movement in combination with the powertrain’s role and application. In addition, Honda emphasizes the new value of electric vehicles. Automobiles which often have an operating rate of about 10 percent can be used as storage batteries (BEV) or generators (FCEV) if they are electric vehicles.
– Honda predicts the use of BEVs for city mobility, and HEVs, PHEVs and FCEVs for long-distance travel.
– The two-motor sports hybrid system Sport Hybrid i-MMD (intelligent Multi Mode Drive) is planned to be used to expand into the small, medium and SUV segments, and core electrification technology is intended to be deployed in the BEV and FCEV sectors. Popularize i-MMD-compatible models to create economies of scale.
– Honda actively advances scalable electrification, including the release of the Clarity’s FCEV, BEV (US only) and PHEV versions built on the same platform.
– The Honda e, a charge / discharge BEV, will be released in Europe in the second half of 2019 and in Japan in 2020.
・In the FCEV sector, Honda has formed a tie-up with GM. In January 2017, Fuel Cell System Manufacturing, the industry’s first fuel-cell system joint venture, was set up in Michigan, USA.
– The facility is set up in GM’s existing battery pack production plant. The mass production of fuel cell systems is scheduled to start around 2020.
– The two companies also cooperate in the self-driving ride share sector.
・Honda recommends to realize carbon-free movement in combination with the powertrain’s role and application. In addition, Honda emphasizes the new value of electric vehicles. Automobiles which often have an operating rate of about 10 percent can be used as storage batteries (BEV) or generators (FCEV) if they are electric vehicles.
– Honda predicts the use of BEVs for city mobility, and HEVs, PHEVs and FCEVs for long-distance travel.
– The two-motor sports hybrid system Sport Hybrid i-MMD (intelligent Multi Mode Drive) is planned to be used to expand into the small, medium and SUV segments, and core electrification technology is intended to be deployed in the BEV and FCEV sectors. Popularize i-MMD-compatible models to create economies of scale.
– Honda actively advances scalable electrification, including the release of the Clarity’s FCEV, BEV (US only) and PHEV versions built on the same platform.
– The Honda e, a charge / discharge BEV, will be released in Europe in the second half of 2019 and in Japan in 2020.
・In the FCEV sector, Honda has formed a tie-up with GM. In January 2017, Fuel Cell System Manufacturing, the industry’s first fuel-cell system joint venture, was set up in Michigan, USA.
– The facility is set up in GM’s existing battery pack production plant. The mass production of fuel cell systems is scheduled to start around 2020.
– The two companies also cooperate in the self-driving ride share sector.
Two-wheeler sector
・In the motorcycle sector, Honda promotes electrification based on long-distance travel in emerging countries and short-distance travel in urban areas. The company envisions battery sharing. – As a test service for short-distance travel, Honda is conducting demonstration experiments in Indonesia deploying battery swap stations that supply batteries. – In April 2019, Suzuki, Yamaha Motor and Kawasaki Heavy Industries announced that they would establish a consortium on exchangeable batteries for electric motorcycles in Japan. The consortium aims to standardize battery specifications and replacement systems in Japan.Other sectors
・Honda is also developing indoor and outdoor logistics and transportation as the last one-mile mobility, and robotics mobility for communication and short-distance movement.Electric Vehicle Strategy
In parallel with the EaaS (Energy as a Service) strategy, Honda is promoting the electrification of mobility. The company plans to promote electrification with an emphasis on BEVs, PHEVs and FCEVs, and plans to increase global sales of electric vehicle to two-thirds of all sales by 2030. In order to achieve this goal, the current two-motor i-MMD (for medium-sized models) has been reduced in size and increased in driving force. Economies of scale are intended to be created by covering a range of vehicle types from compacts to SUVs. I-MMD key technology is also planned to be applied to FCEV and BEV models. The PHEV version of the downsized i-MMD has been on the market since the launch of the 2018 Clarity PHEV. The HEV version is to be installed in the B segment compact hatchback Fit HEV which is scheduled to be released in Japan in the fall of 2019. The company is also actively creating new value for electric vehicles, with a view to using cars that often have an operating rate of around 10 percent as storage batteries (BEV) or generators (FCEV). The BEV model Honda e, to be released in Europe in the second half of 2019, is compatible with charging and discharging. The platform was built from scratch for urban use with weight distribution set at 50:50 in pursuit of good ride comfort and sharp handling.


