AAA weekly
2020-02-03
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Global Smart City Initiatives by Countries, Automakers
Information exchange with infrastructure is indispensable for realizing BEVs, autonomous vehicles and connectivity. For this reason, attention is focused on smart cities that build such places in advance. The definition of “smart city” has yet to be determined; however, Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) defines smart cities as “Optimized sustainable cities or districts where management (planning, maintenance, administration, operation, etc.) is carried out by utilizing new technologies such as ICT for various issues facing the city.” This report provides an overview of smart city initiatives being implemented around the world. According to MLIT, smart city initiatives in Japan are shifting from individual sector-specific approach to cross-sector approach. In order to realize a smart city, it is necessary to optimize the entire region across sectors while constructing systems in individual sectors. In August 2019, the Smart City Public-Private Partnership Platform was established by the Cabinet Office, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and MLIT. The platform promotes smart city initiatives nationwide through public-private partnerships.
* ICT=Information and Communication TechnologyIn the United States, a total of 50 million US dollars has been provided to the city of Columbus, Ohio, which won the Smart City Challenge, a competition for realizing a smart city sponsored by the US Department of Transportation. The project called Smart Columbus promotes connected cars and multimodal mobility.
In Canada, Sidewalk Labs, a subsidiary of Alphabet a Google holding company, is planning a project called Sidewalk Toronto. Traffic and energy data will be constantly collected by sensors embedded throughout the city, and experiments will be conducted toward the creation of future cities using IoT. Despite growing resentment due to concerns about privacy breaches associated with digitalization, Sidewalk Labs released an updated plan reflecting public comments in October 2019. The project’s supervisor Waterfront Toronto, a government’s agency, announced tentative approval of the project in the same month. Automakers are also working on smart city-related projects that use BEVs.
Renault has implemented the world's first smart island project with an energy supplier on the island of Porto Santo, Portugal. Using 40 BEV charging stations and ZOE and Kangoo Z.E. models, the company aims to realize V2G which supplies power from BEVs to the power grid when power demand increases. On the other hand, for charging from the grid, smart charging is enabled so that charging is not performed during times of high electricity rates. The company is also working on reusing BEV batteries.
VW is developing a model zone for electric mobility in Germany. The company combines BEVs and other modes of transportation to build flexible mobility services that meet the needs of local residents. In addition to mobility, VW also plans smart homes and sustainable energy use.
Smart Cities of Japan: Definition and Recent Undertakings
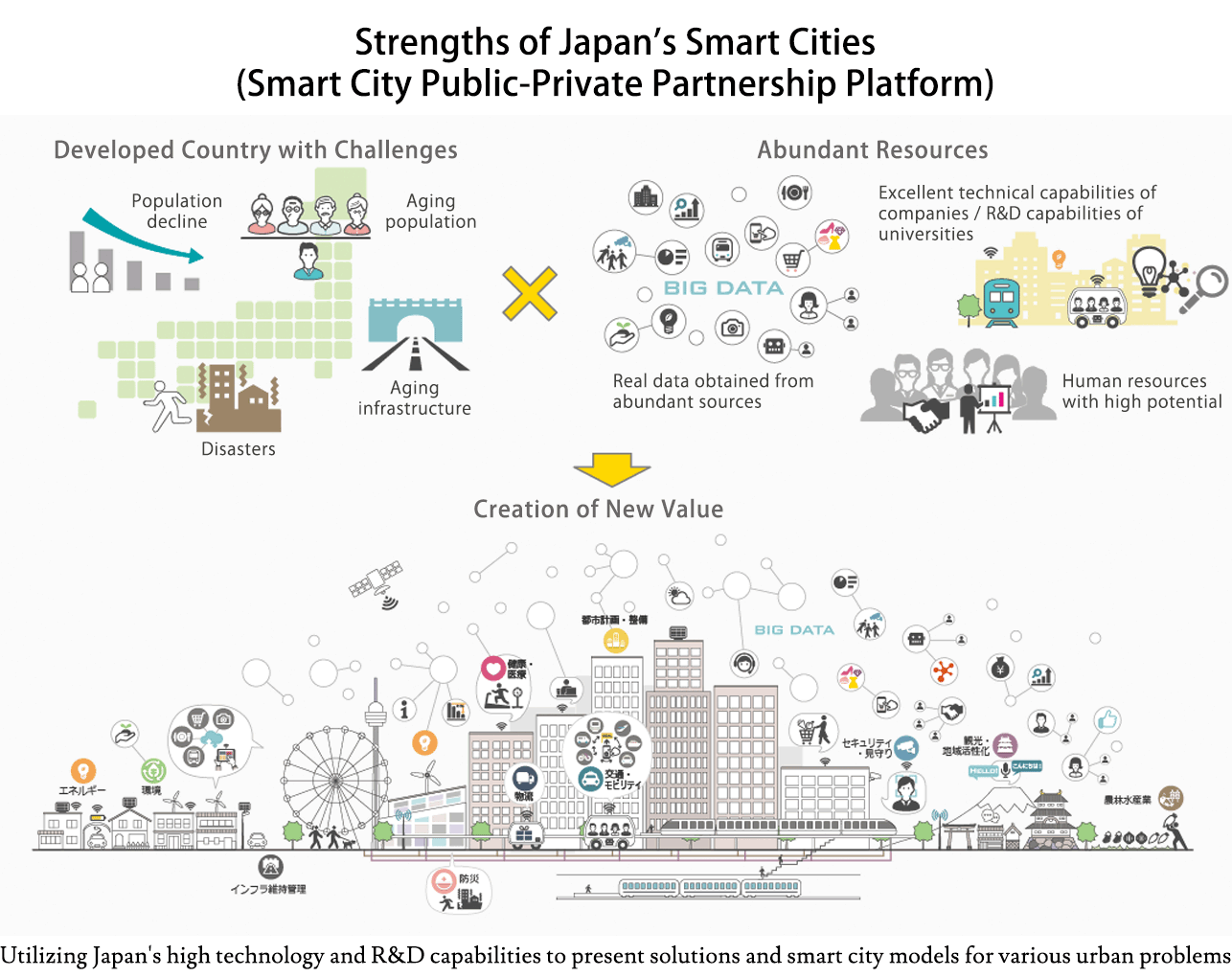
From individual sector-specific approach to cross-sector approach
・The definition of the term “smart city” is currently undefined. – The City Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism defines smart cities as “Optimized sustainable cities or districts where management (planning, maintenance, administration, operation, etc.) is carried out by utilizing new technologies such as ICT for various issues facing the city.” – The Smart City Public-Private Partnership Platform defines smart cities as “By utilizing advanced technologies, efforts are being made to improve the efficiency and sophistication of urban and regional functions and services, solving various issues and creating new value including comfort and convenience. A place for proactive realization of Society 5.0.” ・According to MLIT, smart city initiatives in Japan have been utilizing ICT and data in recent years. The “cross-sector” approach covers a wide range of sectors, such as the environment, energy, transportation, communications, education, medical care and health. – Around 2010, great efforts were made using the “individual sector-specific” for specific sectors such as energy. ・MLIT has stated that the concept of smart city initiatives is to build systems for individual sectors in each region and to optimize cities and regions across sectors.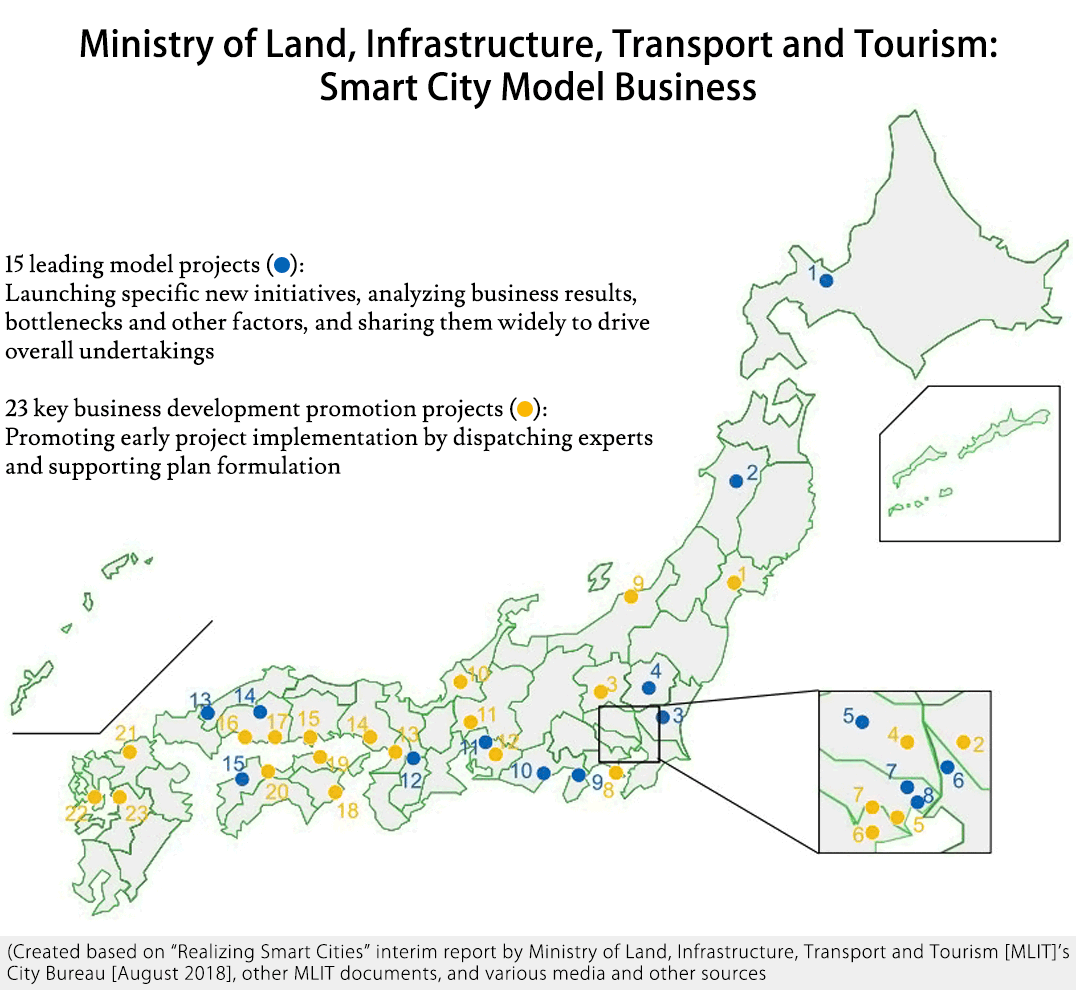
Smart City Public-Private Partnership Platform
・In August 2019, the Cabinet Office, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and MLIT established the “Smart City Public-Private Partnership Platform” to promote smart city initiatives through public-private partnerships. – It is based on the “Integrated Innovation Strategy 2019” determined by the Cabinet in June 2019. – To realize Society 5.0, which is a high-level fusion of cyber and physical, smart cities that utilize new technologies and data such as AI and IoT will be positioned as the basic concept of city development. – As of the end of October 2019, there were 480 members. More specifically, there were 468 organizations (355 enterprises, universities and research institutes, 113 local governments) that engaged in smart city-related business, and 12 related ministries and economic organizations. Companies include Mazda and Denso.MLIT: Smart City Model Business
・In May 2019, MLIT selected and announced advanced model projects for the smart city model business.United States
Smart Columbus
・From the end of 2015 through to 2016, the US Department of Transportation (DOT) held a competition, Smart City Challenge, to improve traffic congestion, crime prevention and citizen services. In June 2016, Columbus, Ohio, was elected as the winning city. The city has proposed improvements to the transportation system with an eye on reducing infant mortality in low-income households. – The Smart City Challenge introduces new technologies, such as connected, autonomous driving, sensors and smart grids, seeking ideas for solving unique city-specific traffic and transportation issues. The recruitment was for medium-sized US cities (population 200,000-850,000). The city with the best proposal was funded to develop and implement the proposal. – A total of 50 million US dollars (including 40 million US dollars from DOT) was provided to the city of Columbus. ・Through Smart Columbus, real-time data is aggregated on a web platform called the Smart Columbus Operating System and used for each project. ・The basic plan, which was revised in 2017, has a total of eight themes under three pillars (technology introduction, user services and new technology development). Themes are as follows: – Environment for connected vehicles: Introducing an environment for connected vehicles, mainly at intersections where accidents frequently occur, and verify the effects. – Multi-modal transfer planning and common payment system: Providing a seamless common payment system for transfer guidance and fares, including sharing. – Smart mobility hub: Wi-Fi will be installed at bus stops and terminals to promote the use of various modes of transportation. – Mobility support for people with cognitive disabilities: Developing a support application that enables people with cognitive disabilities to travel alone.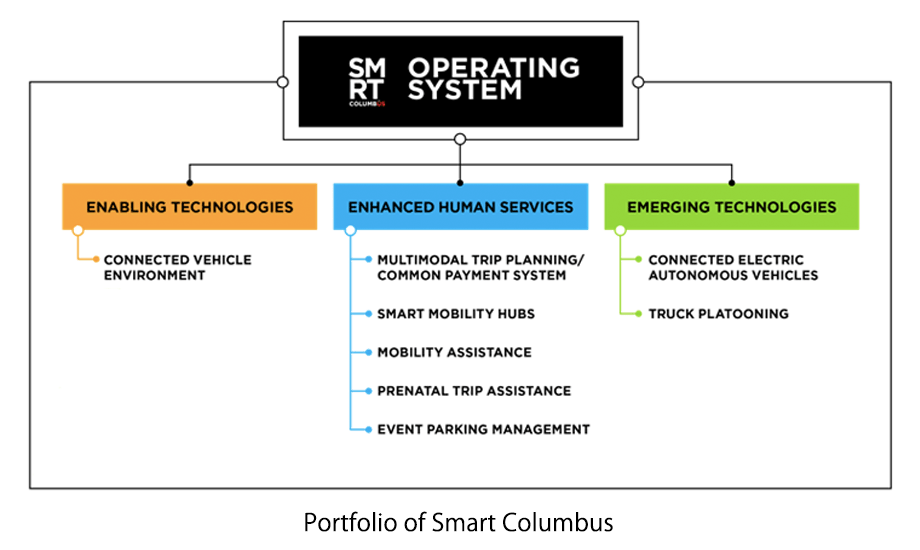 – Mobility support for pregnant women: Providing mobility support services for pregnant women.
– Parking management during events: Introducing a system that can centrally manage information about each parking lot and make reservations in order to be able to cope with congestion during events.
– Connected autonomous-driving BEV: Sequentially introducing a pilot program for a series of use cases.
Introducing a Level 4 self-driving car for specific short-haul routes that are difficult to manage by other means of transportation.
– Truck platooning: Introducing a system that prioritizes connected truck platoons in order to reduce traffic congestion and improve the environment in Columbus which is a logistics base.
・The city of Columbus is promoting the Smart Columbus project in partnership with several companies. AT&T provides various communication technologies and big data analysis technologies, Amazon provides cloud service, NXT and Cohda Wireless provide vehicle-to-vehicle communication technology, Sidewalk Labs provides sensor network, and Continental provides smart intersection transportation system.
– Mobility support for pregnant women: Providing mobility support services for pregnant women.
– Parking management during events: Introducing a system that can centrally manage information about each parking lot and make reservations in order to be able to cope with congestion during events.
– Connected autonomous-driving BEV: Sequentially introducing a pilot program for a series of use cases.
Introducing a Level 4 self-driving car for specific short-haul routes that are difficult to manage by other means of transportation.
– Truck platooning: Introducing a system that prioritizes connected truck platoons in order to reduce traffic congestion and improve the environment in Columbus which is a logistics base.
・The city of Columbus is promoting the Smart Columbus project in partnership with several companies. AT&T provides various communication technologies and big data analysis technologies, Amazon provides cloud service, NXT and Cohda Wireless provide vehicle-to-vehicle communication technology, Sidewalk Labs provides sensor network, and Continental provides smart intersection transportation system.
Smart Dallas
・In 2016, the Dallas Innovation Alliance (DIA), a public-private partnership implementing a smart city program, was launched. January 2018, the project for the second phase of the Smart Cities Living Lab was announced. Main undertakings are as follows: Smart parking that can comprehend traffic volume and availability of parking spaces Public Wi-Fi in Dallas provided by AT&T, Cisco, Nokia and Scientel Solutions – Smart City Digital Infrastructure by AT&T – Smart irrigation using weather dataCanada
Sidewalk Toronto
・In October 2017, Sidewalk Labs, smart city subsidiary of Alphabet which is a holding company of Google, announced a collaborative project “Sidewalk Toronto” with a government agency called Waterfront Toronto. Waterfront Toronto put forth a request for proposals in March 2017 selected Sidewalk Labs for the development of a smart city Toronto’s eastern waterfront. ・The project is intended to create a new local community in the area called Quayside on the eastern waterfront and pilot new technologies for smart cities. – The project is expected to cost 1.3 billion US dollars. – The area will be a place where thousands of people will live, work, learn, play, becoming a place to create and promote new ideas to improve urban life. It is intended to become the world’s first example for reducing living costs, lowering commuting and commuting time, and slashing the city’s carbon footprint.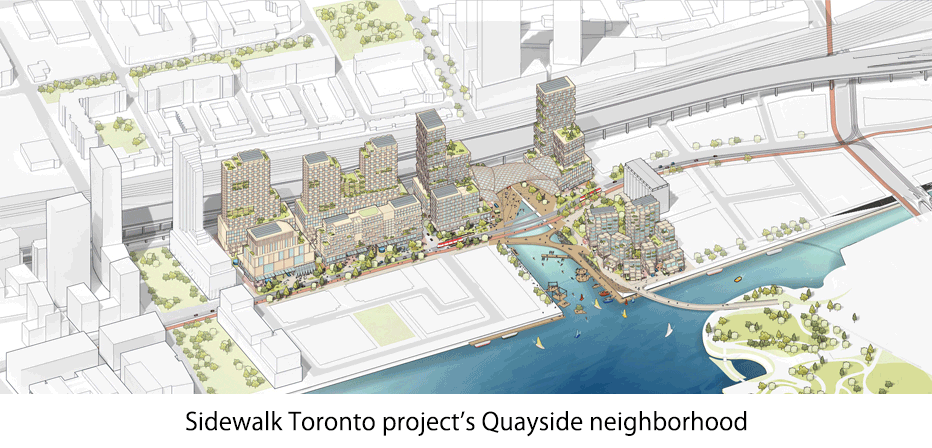 ・Sensors will be embedded throughout the city and information such as traffic flow, air pollution, energy consumption, movement patterns and emissions are constantly collected to create models. IoT’s will be set up at traffic lights and parking lots to analyze traffic flow.
・In October 2019, Waterfront Toronto tentatively approved Sidewalk Labs for going ahead with the project despite concerns over digital projects regarding privacy violations of citizens.
– Sidewalk Labs submitted a plan to Waterfront Toronto in June 2018.
Following feedback from the public, Sidewalk Labs announced a project update in October 2019.
– The area of Quayside is 5 hectares. Sidewalk Labs’ initial plan was to expand the scope of the development, but Waterfront Toronto called for reconsideration, limiting it to 5 hectares.
・Sensors will be embedded throughout the city and information such as traffic flow, air pollution, energy consumption, movement patterns and emissions are constantly collected to create models. IoT’s will be set up at traffic lights and parking lots to analyze traffic flow.
・In October 2019, Waterfront Toronto tentatively approved Sidewalk Labs for going ahead with the project despite concerns over digital projects regarding privacy violations of citizens.
– Sidewalk Labs submitted a plan to Waterfront Toronto in June 2018.
Following feedback from the public, Sidewalk Labs announced a project update in October 2019.
– The area of Quayside is 5 hectares. Sidewalk Labs’ initial plan was to expand the scope of the development, but Waterfront Toronto called for reconsideration, limiting it to 5 hectares.

