AAA weekly
2020-02-10
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
China Implements New Foreign Investment Law in 2020
When a foreign-affiliated company sets up an equity or contractual joint venture in China, it must comply with Chinese foreign investment laws and regulations. With the implementation of China’s “Reform and Open Door” policy, the Chinese government enacted the first law on foreign investment the Sino-foreign Equity Joint Ventures Law in 1979. It was followed by the Foreign-capital Enterprises Law in 1988 and the Sino-foreign Contractual Joint Ventures Law in 1988. They are collectively called the “Three Foreign-invested Enterprises Laws” or “Three FIE Laws.” In response to changes in the economic environment and actual foreign investment, relevant laws and regulations have been revised several times. In March 2019, the National People’s Congress adopted the Foreign Investment Law which is the successor to the Three FIE Laws. The new law went into effect in January 2020. The Three FIE Laws have been abolished and integrated into the Foreign Investment Law. This report introduces the basics of laws and regulations on foreign investment in China based on the progress of the revision of the Three FIE Laws.
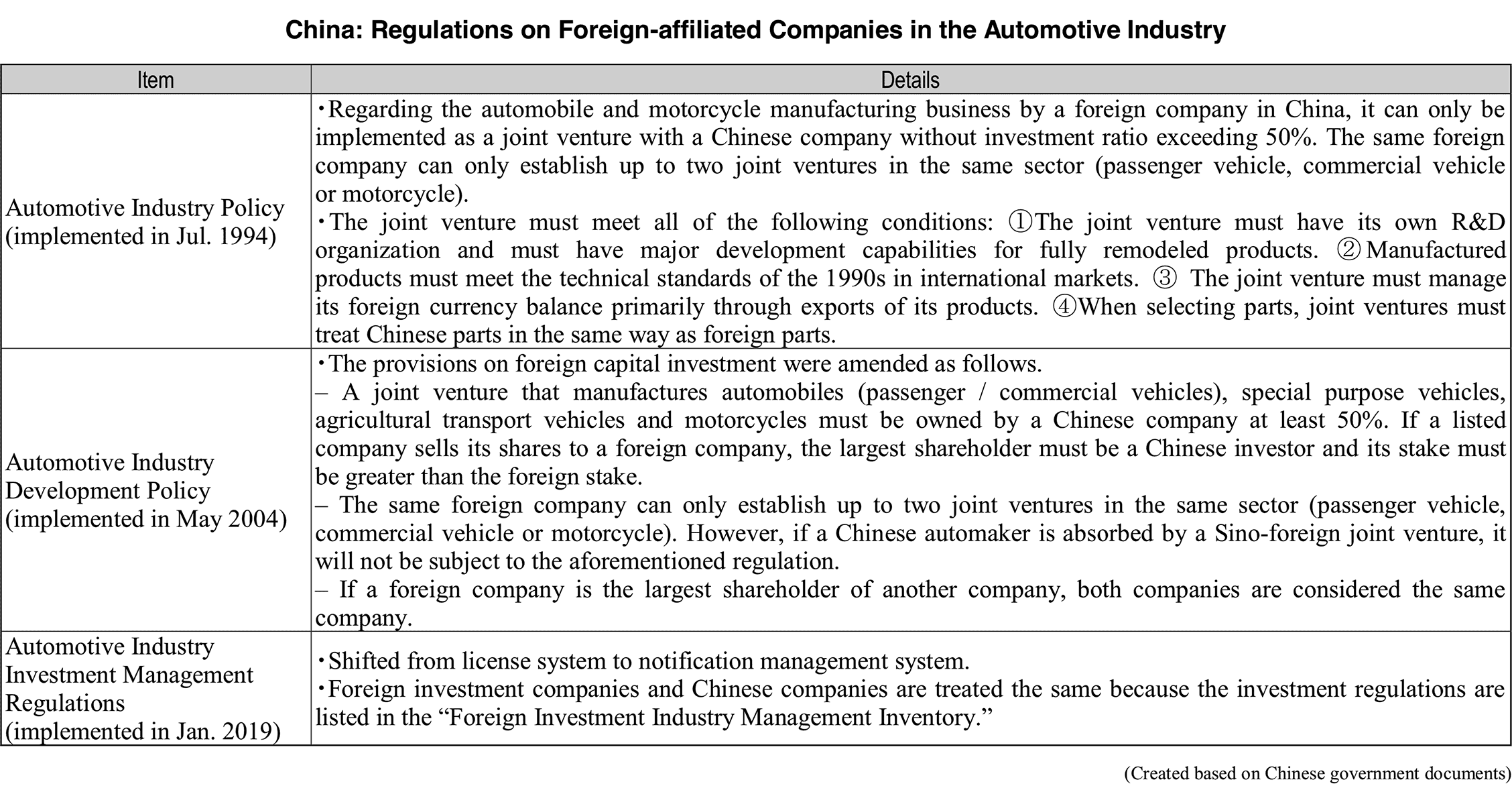
Regarding automobile manufacturing, there are regulations that restrict foreign ownership up to 50% and up to two joint ventures in the same vehicle sector. Foreign companies operating in the automotive industry in China have no choice but to create joint ventures, but the Chinese government has stated that it will remove all relevant regulations by 2022. It is possible that foreign companies will be allowed to have higher investment ratio and to set up wholly-owned subsidiaries in China.
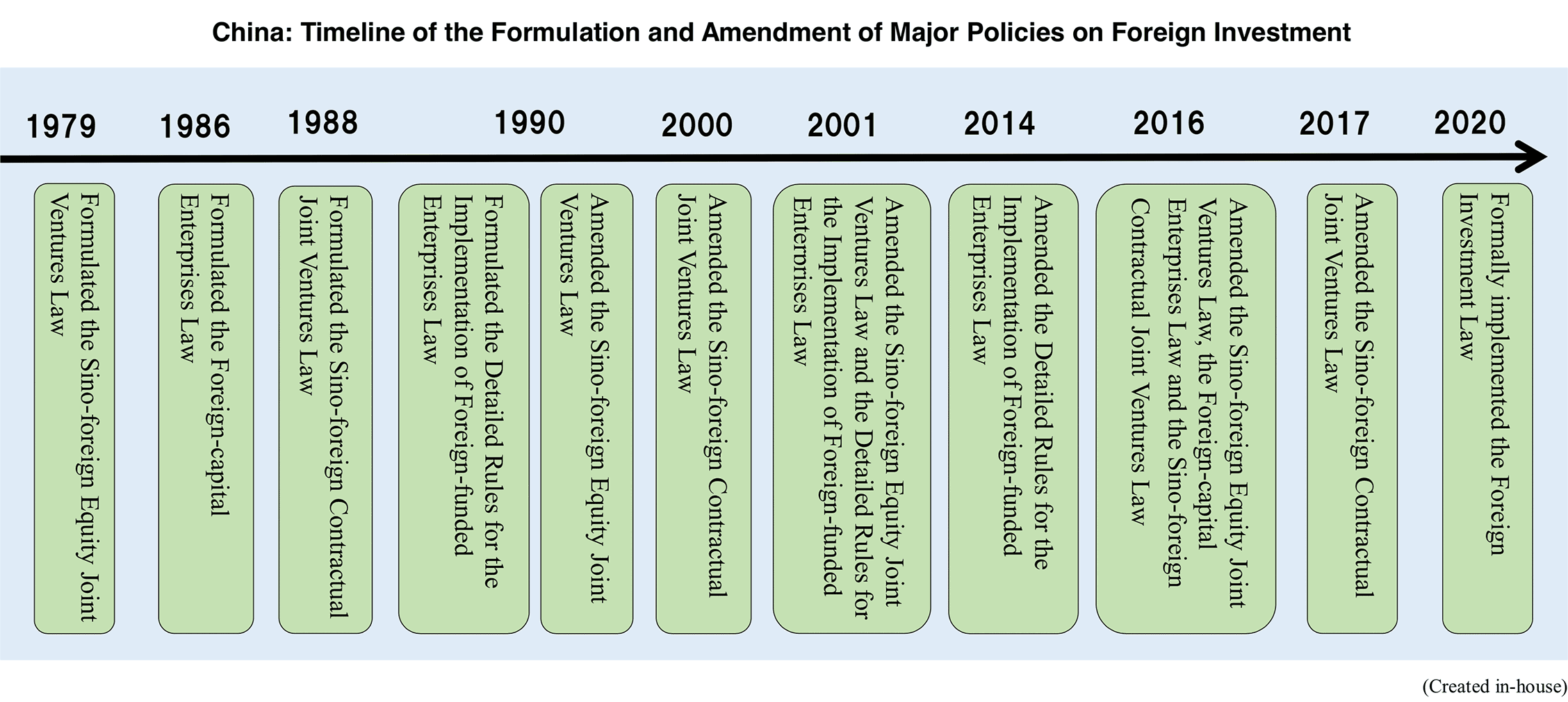
To strengthen the effective use of foreign capital and unify the basic laws of foreign investment, the Chinese government enacted the Foreign Investment Law in March 2019, replacing the Three FIE Laws and becoming the basic law of foreign investment. The new law went into effect in January of 2020.
The provisions of the law include several topics of interest to foreign companies: “When enacting laws and regulations concerning foreign investment in the future, the opinions and proposals of foreign companies must be taken into account” (Article 10), “foreign-affiliated companies should participate equally in standard settings” (Article 15), “guarantee the fair participation of foreign-affiliated companies in government procurement activities” (Article 16) and “being able to freely remit foreign investors’ profits, capital returns, and the like overseas in Chinese yuan or foreign currency in accordance with the law” (Article 21). In addition, regarding the issue of technology transfer, which has attracted attention due to the Sino-US trade conflict, Article 22 states that “The State shall protect the intellectual property rights of foreign investors and foreign-funded enterprises, and protect the legitimate rights and interests of holders of intellectual property rights and relevant right holders; in case of any infringement of intellectual property right, legal liability shall be investigated strictly in accordance with the law.”
The manufacturing and development capabilities of the entire Chinese automobile industry is expected to improve by attracting foreign capital investment in related fields, and encouraging local manufacturing and R&D of related products.
China: Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China
(Implemented in Jan. 2020)
Chapter I: General Provisions
Article 1
The Foreign Investment Law of the People's Republic of China (hereinafter referred to as "the Law") is hereby formulated in accordance with the Constitution of the People's Republic of China in a bid to further expand opening-up, vigorously promote foreign investment, protect the legitimate rights and interests of foreign investors, standardize the management of foreign investment, impel the formation of a new pattern of all-round opening-up and boost the sound development of the socialist market economy.
Article 2
The Law shall be applicable to the foreign investment within the territory of the People's Republic of China ("the territory of China").
For the purpose of the Law, foreign investment refers to the investment activity directly or indirectly conducted by a foreign natural person, enterprise or other organization (the "foreign investors"), including the following circumstances:
1. A foreign investor establishes a foreign-funded enterprise within the territory of China, independently or jointly with any other investor;
2. A foreign investor acquires shares, equities, property shares or any other similar rights and interests of an enterprise within the territory of China;
3. A foreign investor makes investment to initiate a new project within the territory of China, independently or jointly with any other investor; and
4. A foreign investor makes investment in any other way stipulated by laws, administrative regulations or provisions of the State Council.
For the purpose of the Law, a foreign-funded enterprise refers to an enterprise that is incorporated under the Chinese laws within the territory of China and is wholly or partly invested by a foreign investor.
Article 3
The State shall adhere to the basic state policy of opening-up and encourage foreign investors to make investments within the territory of China.
The State shall implement policies on high-level investment liberalization and convenience, establish and improve the mechanism to promote foreign investment, and create a stable, transparent, foreseeable and level-playing market environment.
Article 4
The State shall implement the management systems of pre-establishment national treatment and negative list for foreign investment.
For the purpose of the preceding paragraph, pre-establishment national treatment refers to the treatment given to foreign investors and their investments during the investment access stage, which is not lower than that given to their domestic counterparts; negative list refers to special administrative measures for the access of foreign investment in specific fields as stipulated by the State. The State shall give national treatment to foreign investment beyond the negative list.
The negative list will be issued by or upon approval by the State Council. If more preferential treatment concerning access is offered to a foreign investor under any international treaty or agreement that the People's Republic of China concludes or joins in, relevant provisions in such treaty or agreement may prevail.
Article 5
The State shall protect foreign investors' investment, earnings and other legitimate rights and interests within the territory of China in accordance with the law.
Article 6
Foreign investors and foreign-funded enterprises carrying out investment activities within the territory of China shall observe the Chinese laws and regulations, and shall not impair China's security or damage any public interest.
Article 7
The competent departments for commerce and investment under the State Council shall, pursuant to the division of duties, promote, protect and manage foreign investment; other relevant departments under the State Council shall take charge of the relevant work in the promotion, protection and management of foreign investment within the scope of their respective duties.
The relevant department under the local people's government at or above the county level shall carry out the work relating to promotion, protection and management of foreign investment in accordance with laws and regulations and in line with the division of duties determined by the people's government at the same level.
Article 8
Employees of a foreign-funded enterprise shall, pursuant to the law, establish trade union, carry out trade union activities, and safeguard their legitimate rights and interests. A foreign-funded enterprise shall provide necessary conditions for its trade union to carry out relevant activities.
Chapter II: Investment Promotion
Article 9
All national policies on supporting the development of enterprises shall equally apply to foreign-funded enterprises in accordance with the law.
Article 10
Comments and suggestions from foreign-funded enterprises shall be sought in a proper manner when formulating laws, regulations and rules relating to foreign investment.
Normative documents and judgment documents relating to foreign investment shall be published in accordance with the law in due time.
Article 11
The State shall establish and perfect the service system for foreign investment, and provide foreign investors and foreign-funded enterprises with consultation and services in respect oflaws and regulations, policies and measures, investment project information and other aspects.
Article 12
The State shall establish multilateral andbilateral cooperation mechanisms for the promotion of investment with other countries, regions and international organizations, so as to enhance international exchanges and cooperation in terms of investment.
Article 13
The State may, as needed, establish special economic area or carry out pilot polices and measures on foreign investment in specific areas, so as to promote foreign investment and expanding opening-up.
Article 14
The State may, according to the requirements of national economy and social development, encourage and guide foreign investors to invest in specific industries, fields and areas. Foreign investors and foreign-funded enterprises may enjoy preferential treatments in accordance with laws, administrative regulations or provisions of the State Council.
Article 15
The State shall guarantee that foreign-funded enterprises can equally participate in setting standards in accordance with the law, and enhance information disclosure and social supervision on standard setting. The compulsory standards formulated by the State shall equally apply to foreign-funded enterprises.
Article 16
The State shall guarantee that foreign-funded enterprises can participate in government procurement activities through fair competition. Products produced and services provided by foreign-funded enterprises within the territory of China shall be treated equally in government procurement.
Article 17
Foreign-funded enterprises may conduct financing through public offering of shares, corporate bonds and other securities or by other means.
Article 18
Local people's governments at county level or above may, in accordance with the provisions in laws, administrative regulations or local regulations, formulate policies on promotion and facilitation of foreign investment within their respective statutory authorities.
Article 19
People's governments at all levels and relevant departments thereunder shall, under the principle of convenience, efficiency and transparency, streamline procedures for handling affairs, raise their efficiency and optimize government services, so as to further improve the services offered for foreign investment.
Relevant competent departments shall prepare and publish guidelines for foreign investment and provide foreign investors and foreign-funded enterprises with services and convenience.
Please
register or subscribe to view this report for free.
If you’re already a subscriber, sign in.
Credit card information is not needed for free trial registration.
You are eligible to view one report for free.
Additional reports require subscription.



