AAA weekly
2021-12-27
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Toyota Motor’s Battery Strategy Until 2030
| This report includes information on the following topics: | Key images: |
|---|---|
|
|
Toyota Motor announced its battery strategy for the popularization of electric vehicles until 2030 in September 2021. The company plans to invest 1.5 trillion JPY in strengthening research and development of drive batteries and building a battery supply system to promote the diffusion of electric vehicles. Toyota has set a goal of reducing the battery cost per BEV by 50% in the latter half of the 2020s in order to promote electric vehicles. The automaker intends to increase competitiveness by reducing the cost of the battery itself and improving the electricity cost by improving the efficiency of the entire vehicle.
Toyota Motor: Electric Vehicle and Battery Development Strategy
Electric Vehicle Strategy
Electric vehicle sales target
・Toyota plans to globally sell 8 million electric vehicles, including 2 million ZEVs (BEV + FCEV) by 2030 toward the realization of carbon neutrality in 2050. - HEVs will continue to be the axis of the strategy, but powertrains will be selected for each market depending on their effect on reducing CO2 through Well to Wheel under local conditions. - In markets where the ratio of power generation from renewable energy is low, Toyota will promote HEVs. On the other hand, in markets where renewable energy is widespread, ZEVs will be promoted.CO2 reduction by HEVs
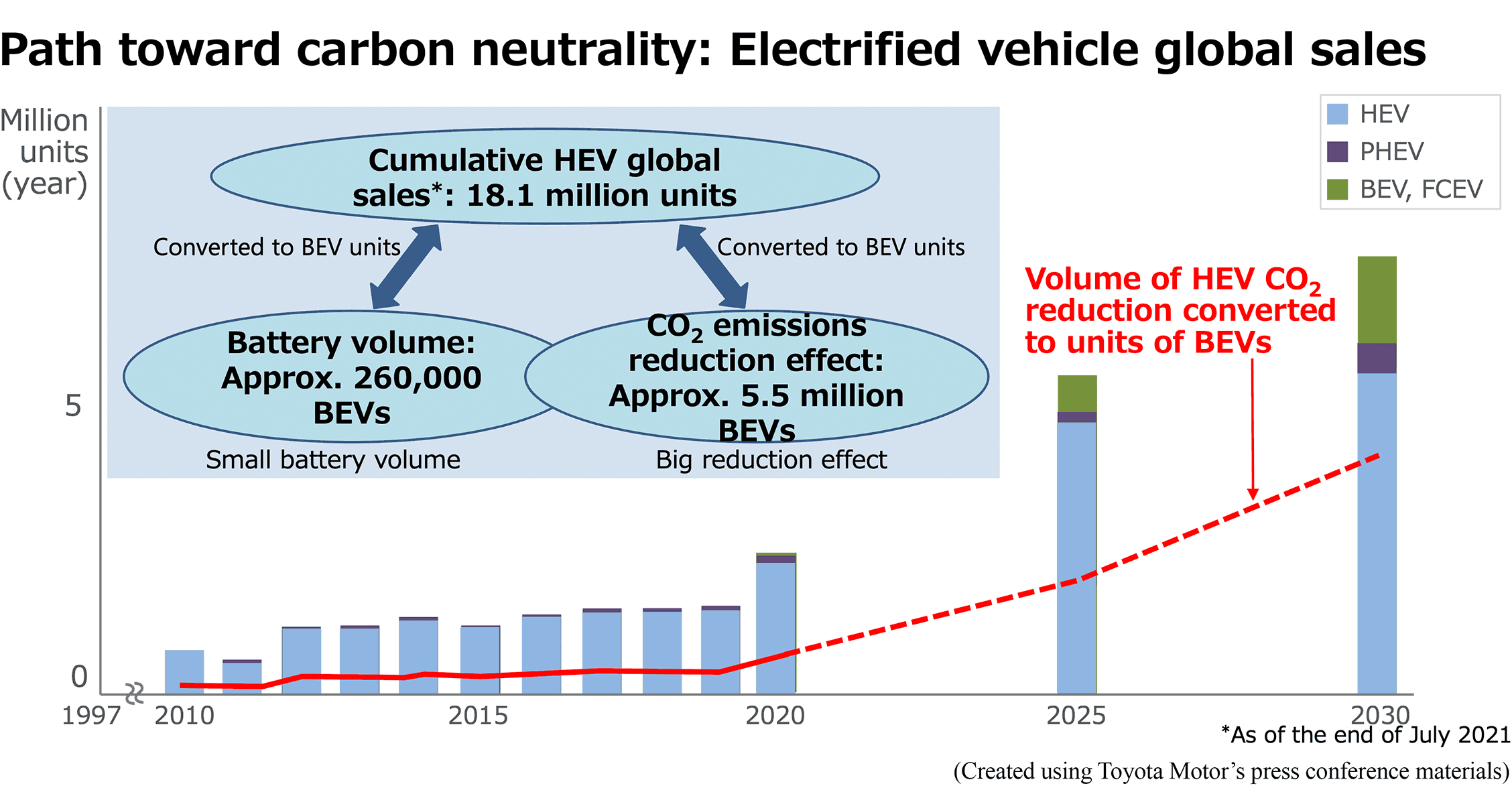
・Regarding the CO2 emission reduction effect of HEVs, Toyota said that three HEVs have the same reduction effect as one BEV. - According to Toyota's estimates, the cumulative global sales of HEVs (18.1 million units as of July 2021) correspond with the battery volume of approx. 260,000 BEVs and the CO2 emissions reduction effect of approx. 5.5 million BEVs. - Toyota intends to utilize HEVs, which have a high CO2 reduction effect, to lower CO2 emissions in emerging countries and to reduce global emissions by further improving the performance of HEVs.Battery Strategy for Disseminating Electric Vehicles
Expansion of battery lineup
・Toyota plans to develop batteries for various electric powertrains to increase battery options with the aim of improving the performance of HEVs and other electric vehicles. - For HEVs, Toyota is promoting the development of batteries that emphasize the instantaneous power of charging and discharging. The automaker will continue developing nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion batteries. - For BEVs and PHEVs, Toyota will develop large-capacity lithium-ion batteries with an emphasis on endurance. - Toyota will develop a new-structure lithium-ion batteries including an solid-state batteries and utilize them for electric powertrains.Battery cost reduction measures
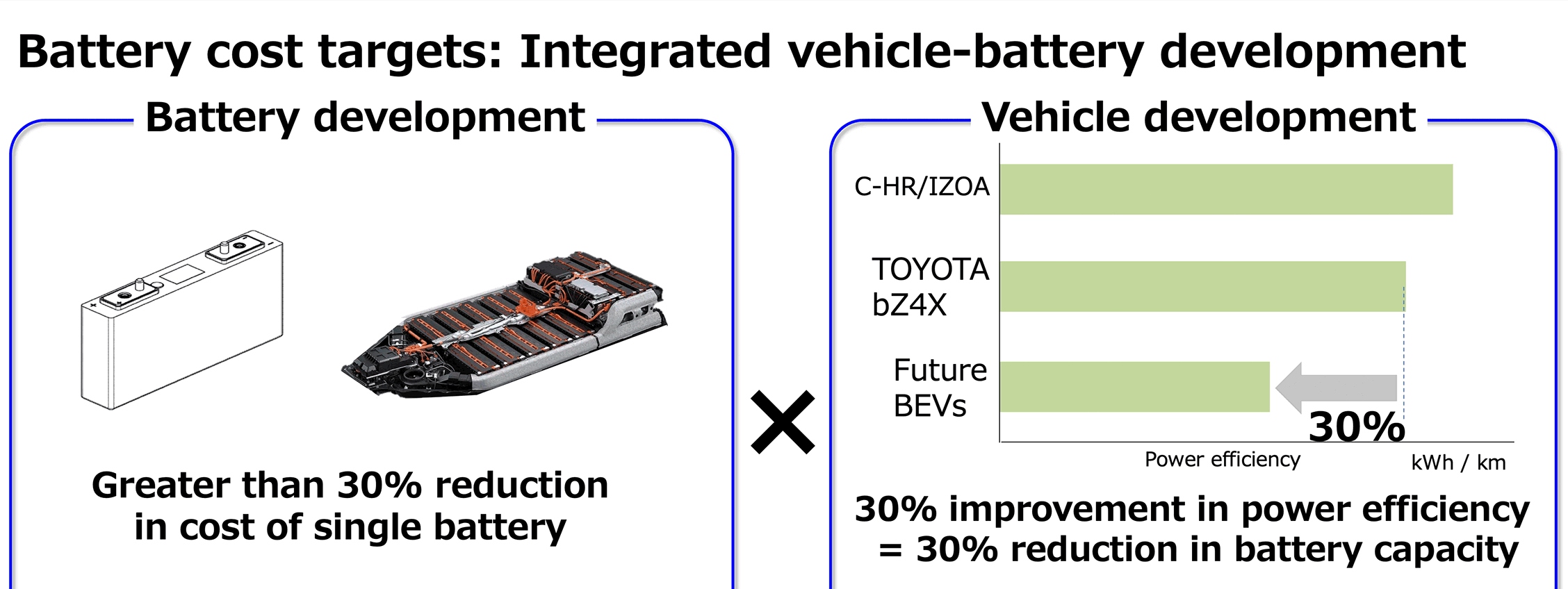
・Toyota aims to popularize electric vehicles, emphasizing efforts to reduce the cost of drive batteries, which have a large cost reduction effect. - In order to reduce the cost of a single battery, Toyota will improve the efficiency of the battery by reducing the amount of precious metal used and improving control. Ultimately, Toyota aims to reduce the cost of the battery alone by 30% or more. - By reducing the running resistance of the vehicle and regenerative control, and improving the efficiency of the drive system, the electricity cost of the vehicle will be improved and the amount of batteries installed will be reduced. Toyota aims to reduce the installed battery capacity by 30% by improving the electricity cost of vehicles by about 30%. - Toyota aims to reduce the battery cost per BEV by 50% by the latter half of the 2020s by improving the battery and reducing the electricity cost by raising the efficiency of the entire vehicle.

