AAA weekly
2019-10-21
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Waymo and Handful of Other Startups Continue to Dominate the Sector
There are still lots of hurdles in the way to achieve level 4 or higher self-driving. Startups such as America’s Waymo and China’s Pony.ai have made a good track record in public road tests, but a few companies even suspended operations. OEMs heavily rely on these startups and software companies in Israel and India for autonomous driving development.
According to a test report (hereinafter referred to as a report) on autonomous driving vehicles issued in February 2019 by the California’s DMV (Department of Motor Vehicles), Waymo’s self-driving vehicle has traveled 18,000km without human intervention, putting pressure on other companies. In addition, the company’s performance in 2017 doubled, indicating high development capabilities.
GM Cruise, a subsidiary of GM, announced its Cruise AV, a Level 4 autonomous vehicle that does not have a pedal or other control device, in January 2018. At the same time, the company revealed that the model is scheduled to be launched in 2019. In order to let the vehicle run on public roads, the automaker submitted an application to NHTSA (National Road Traffic Safety Administration) for an exemption from safety standards for ordinary automobiles. In August 2019, Waymo also sent a letter to NHTSA requesting that the application be accepted.
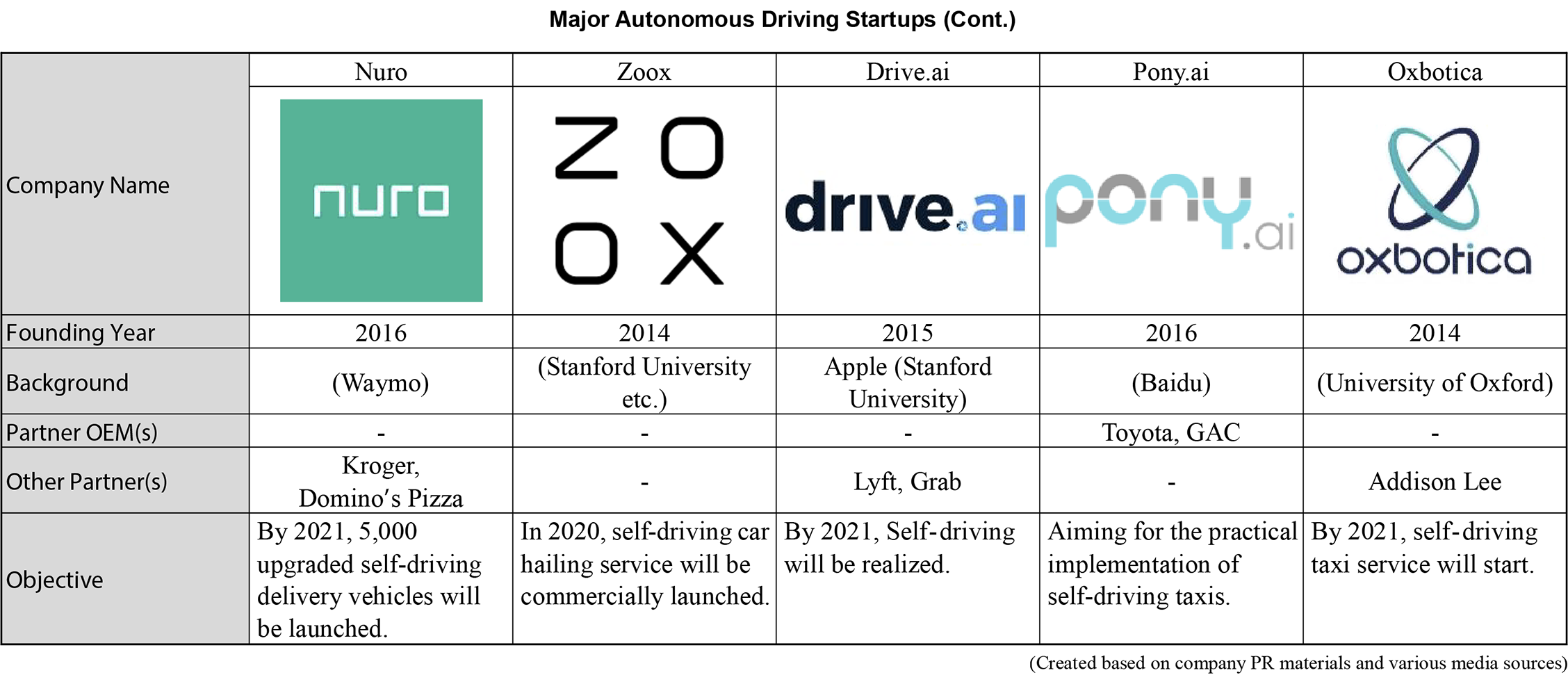
In the autonomous driving sector, many startups cooperate with the parent company or partner OEMs to develop self-driving vehicles, but there are also companies that develop self-driving vehicles independently. Nuro has developed a vehicle for package delivery, and Zoox has developed a vehicle for unmanned taxi service.
On the other hand, there are also some negative trends in the industry. Roadstar.ai, which was ranked 10th by California’s DMV in 2018, is reported to virtually cease to exist as of June 2019. Meanwhile, Drive.ai of Stanford University was driven out of business due to financial difficulties. The company was eventually acquired by Apple. Apple is expected to increase the performance of Apple Car by introducing Drive.ai personnel to the autonomous driving project Titan.
Startups with Significant Contribution to the Development of Autonomous Driving
Autonomous driving startups in Silicon Valley
・Autonomous-driving startups are concentrated in Silicon Valley, USA. – In the vicinity of Silicon Valley, a number of autonomous-driving tests are also underway. ・The California Department of Motor Vehicles publishes “Autonomous Vehicle Disengagement Reports” every year, which summarizes the test status of self-driving vehicle developers. – It summarizes the frequency of the system switching to manual operation to ensure safety and intervention operation performed by the driver. – The 2018 report released in February 2019 summarizes the public road tests of 467 vehicles from 28 companies conducted in the state from December 2017 to November 2018. The reports are based on information* released by the companies. (*Note that experimental conditions and intervention criteria are not standardized, so strict comparison is not possible.) ♦ A startup Pony.ai occupies the fifth place and it is significantly ahead of sixth-placed Nissan. In addition, Waymo can run about 18,000 km without intervention which is more than twice compared to the performance of GM Cruise in the second place. ♦ Only the top two companies, Waymo and GM Cruise, as well as the lower two companies, Uber and Apple, exceeded 20 test vehicles. Of all the 143,720 interventions reported in the 2018 edition, Apple accounts for 69,510 and Uber accounts for 70,165.Autonomous Vehicle Disengagement Reports (Excerpt, 2018)
| Ranking | Company Name | Distance traveled per intervention* (km) | Number of interventions per 1,000 km (times) | Number of vehicles (units) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Waymo | 17,846.8 | 0.06 | 111 |
| 2 | GM Cruise | 8,327.8 | 0.12 | 162 |
| 3 | Zoox | 3,076.4 | 0.33 | 10 |
| 4 | Nuro | 1,645.3 | 0.61 | 13 |
| 5 | Pony.ai | 1,635.6 | 0.61 | 6 |
| 6 | Nissan | 336.8 | 2.97 | 4 |
| 10 | Roadstar.ai | 280.5 | 3.56 | 2 |
| 27 | Apple | 1.8 | 544.78 | 62 |
| 28 | Uber | 0.6 | 1,630.29 | 29 |
Autonomous driving startups in China
・In addition to the above-mentioned Pony.ai, Roadstar.ai and WeRide.ai are active in China among others. In addition, AutoX, founded in Silicon Valley, is based in Hong Kong. In August 2019, the company announced its plan to build the first robot taxi test zone in Shanghai, China. ・Roadstar.ai, which was working on level 4 autonomous driving technology development, was reportedly no longer in operation as of June 2019. – The company was established in May 2017 by three engineers from Baidu in Shenzhen, China. One of the founders was dismissed in January 2019 for financial fraud, data creation and power harassment. The other two founders could not be found at the company either and the company’s office had no staff as of June 2019. – A press release announced in May 2018 stated the following plan. ♦ As an ambitious goal for 2020, driver intervention rate for autonomous vehicles will be reduced to once per 1,000 km of driving. ♦ By 2019, it will jointly produce 200 self-driving cars with several automakers. By 2020, 1,500 autonomous driving EVs for dispatch services will be placed in the center of Tier 1 cities. – It was ranked 10th out of 28 companies in the 2018 test status report by California Department of Motor Vehicles.Autonomous driving startups in Europe
・In addition to Oxbotica (UK) that spun out from University of Oxford, there are also AImotive (Hungary) and FiveAI (UK).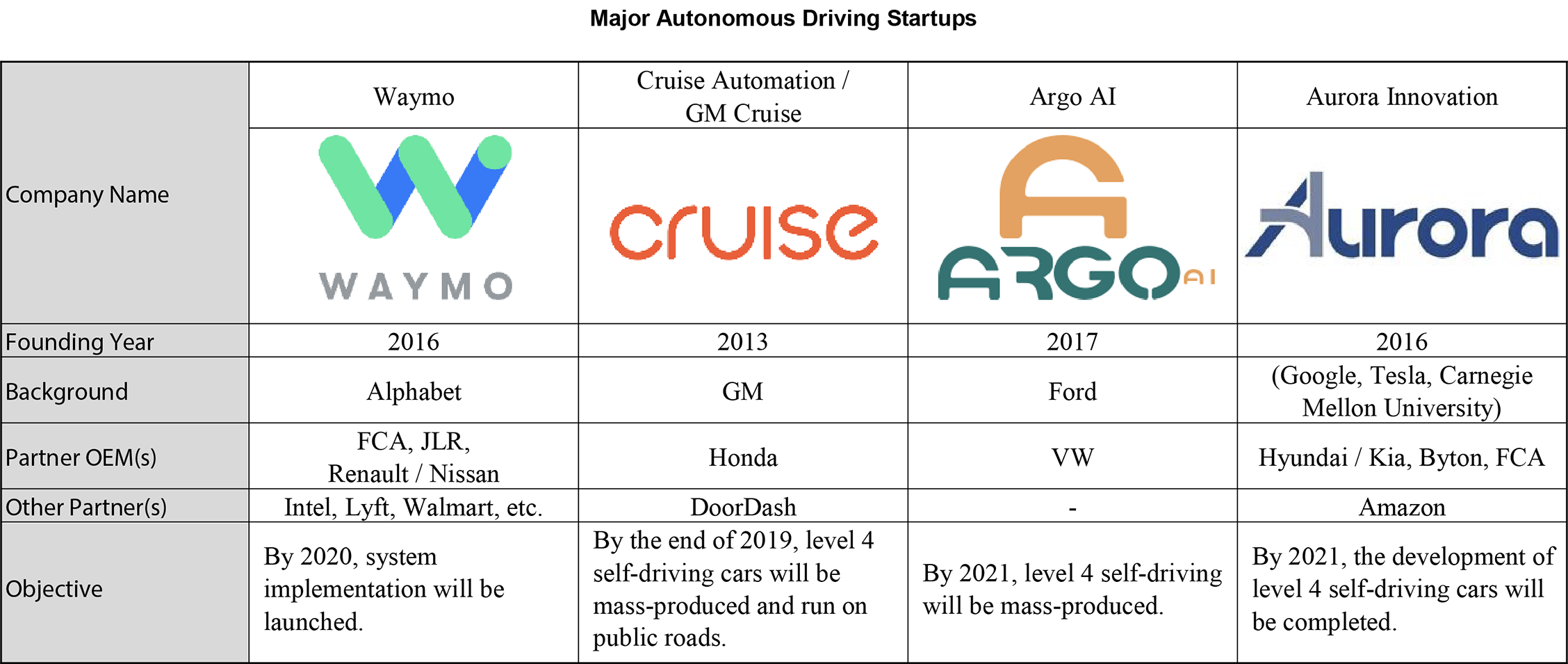
Autonomous Driving Startups: Company History
Waymo
・The company was established in December 2016 as an independent company from the autonomous driving development department of Google (Alphabet). It is located in Mountain View, California. – Google launched the Self-Driving Car project in 2009. – In May 2016, Google partnered with FCA. ・In 2017, 100 self-driving cars based on Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid were introduced as test vehicles. This was the first time to build a self-driving vehicle based on a mass-production model. ・In March 2018, the company partnered with Jaguar Land Rover. – An autonomous driving vehicle based on the Jaguar I-PACE will be developed and a maximum of 20,000 vehicles will be introduced as test vehicles within a few years. ・In May 2018, the company expanded partnership with FCA. – 62,000 autonomous driving vehicles based on the Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid were added. ・In July 2018, the company partnered with multiple companies, including retailer Walmart. – Pilot programs were implemented for customers of various business types. ・In May 2019, the company partnered with ride hailing company Lyft. ・In June 2019, the company signed an exclusive contract with Renault - Nissan for unmanned mobility services. – The company is considering service development in France and Japan. ・The company is aiming to put the system into practical use by 2020.Cruise Automation / GM Cruise


