AAA weekly
2019-10-21
Copyright FOURIN, Inc. 2025
Škoda Auto Shifts Focus to Mobility Services, Digital Solutions
VW Group's Škoda Auto has entered more than 100 markets, with a focus on Europe and China, passenger car sales volume reaching 1.25 million units in 2018. In anticipation of the future transformation of automakers from vehicle manufacturers to mobility service providers, Škoda Auto plans to invest a total of 2 billion EUR in the next five years from 2019 in technology and service development, and the construction of new business models in the areas of e-mobility and connected / mobility services.
Škoda Auto: Overview of Management / Technology Strategy
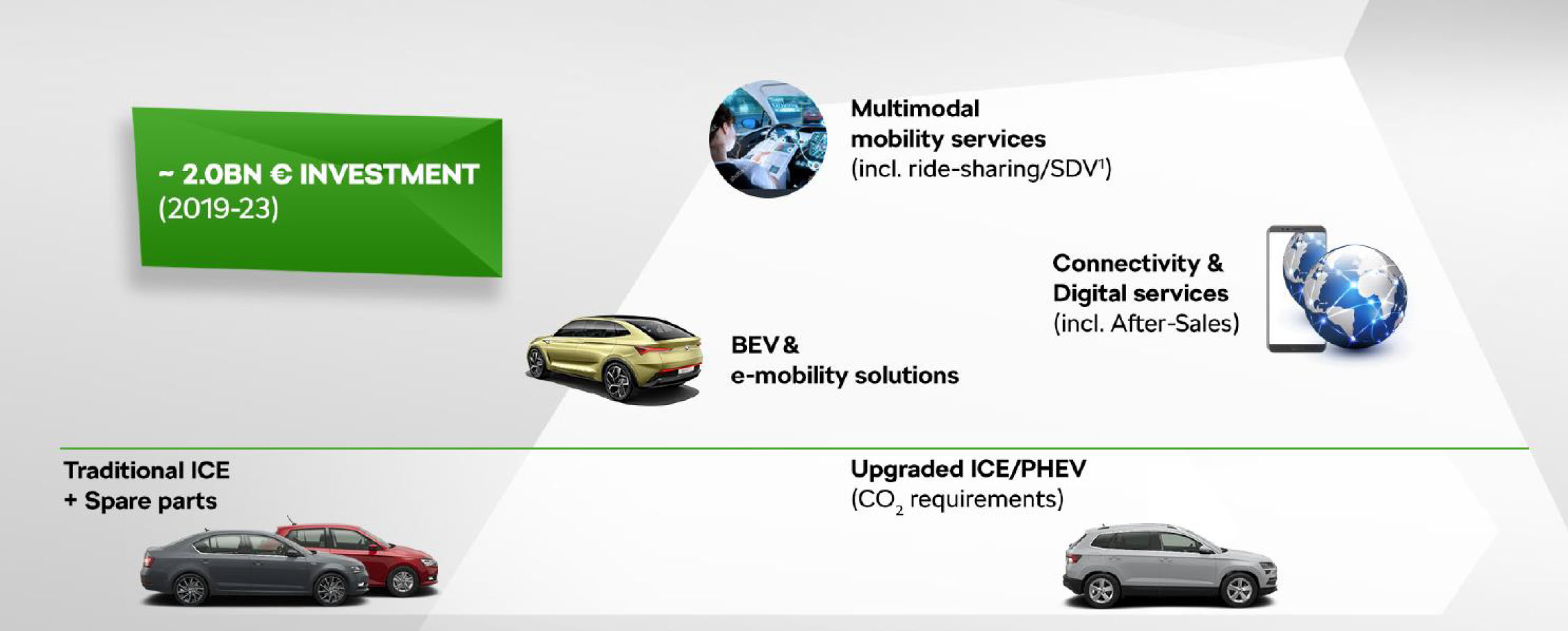
| Area / Overview | Details / Trends |
|---|---|
| Investment in strategic areas | From 2019 to 2023, the company plans to invest 2 billion euros in BEV / E-mobility solutions, connected / digital services and mobility services. Based on sales and service of ICEVs, improvement of ICE technology (including CNG) and hybrid technology (PHEV, MHEV), the company will add new technologies, business models and promote business transformation. |
| Strategy 2025 | Aiming to increase sales and profits and cultivate new businesses to achieve a target of ROS of seven percent or higher in 2025: SUV lineup expansion, promotion of E-mobility, global expansion, promotion of digitalization. |
| Expansion of SUV lineup | Previously only the old PQ35 platform-based Yeti 1 model was introduced, but from 2017 to 2019 three models are scheduled to be launched, the MQB-based small, compact and medium models. The Karoq model (compact, based on MQB A1, successor of the Yeti) was introduced at the end of 2017, and the Kodiaq (based on MQB A2, sister model of Tiguan LWB) was launched in March 2017. The Kamiq (subcompact, based on MQB A0) was released in June 2018, and the Kodiaq GT (high performance specification) was introduced in October 2018 in China. In 2019, the Kodiaq RS (high performance specification) and the Kamiq are scheduled to be introduced in Europe, and the Kamiq GT (China version) in China. |
| Electric vehicles | From 2019, the company plans to launch multiple MQB-based PHEVs and MEB-based BEVs. Production of Citigo’s BEV (shares system with the e-up) and Superb PHEV (shares system with the Passat GTE) started in 2019. In 2020, a MEB-based SUV BEV (Vision E / iV concept-based) will be launched. The company plans to commercialize a 48V MHEV (based on Vision X) CNG engine. Škoda Auto plans to launch 10 EVs in 2022 (including PHEV and MHEV) and another 10 EV models in 2025 (6 BEV models, 4 PHEV models). EV sales ratio is expected to reach 25 percent in 2025. The EV model name “iV” is adopted as a sub-brand. |
| Connected / digitalized | Škoda Auto is introducing next-generation connected infotainment system (new models to be equipped from 2019 and EVs from 2020). The company provides support for next-generation communication (after 2019) and OTA software update function (after 2020). Functions include fleet management services, data business, smart subscription, revenue share, location-based service proposals among others. The company promotes the use of Industry 4.0 solutions in manufacturing and logistics. |
| Mobility solutions | Škoda Auto is aiming to develop new services and establish a business model through collaboration between Škoda Auto DigiLab (headquartered in Prague with offices in Tel Aviv and Beijing) and external IT experts and startups. The automaker is shifting from vehicle manufacturing to mobility service provider, services including vehicle sharing, ride sharing, multimodal mobility app and safety / autonomous driving support technology among others. |
| Utilizing modular architecture | The ratio of MQB-based models: 40 percent in 2015, 65 percent in 2018, 70 percent in 2020 and up to 80 percent in 2025. The company plans to deploy the production of models with the same architecture at each factory. The MEB platform is also actively used. |
| Global expansion | The company’s policy is to double business in China while securing profits. Škoda Auto controls operations in India and Russia within the VW Group. In India, the company leads the India 2.0 project aimed at launching MQB A0-based strategic vehicles and strengthening local R&D. |
Škoda Auto uses high-performance powertrain technology of the VW Group. While excelling in quality and durability, the Škoda brand maintains its advantage of lower prices compared to the VW brand. Škoda Auto is focusing on developing solutions for connected services that lead to added value while aiming for improved competitiveness. The company also actively engages in MaaS (Mobility as a Service) schemes including BEV sharing, ride sharing, optimal route finder apps, transportation search, boarding and payment. Škoda Auto’s subsidiary Škoda Auto DigiLab is developing mobility solutions and services through collaboration external IT experts and startups. The company is headquartered in Prague with additional offices in Tel Aviv and Beijing. Škoda Auto is also responsible for sharing results in the areas of connected and mobility services.
In the electric vehicle sector, the company plans to commercialize a MEB-based BEV in addition to the mass production of a MQB-based PHEV. The company intends to provide new mobility services while making full use of VW's technological capabilities and responding to stricter CO2 regulations. Škoda Auto also attaches importance to internal combustion engine technology and is making efforts to develop CNG-related technologies such as improving the performance of CNG engines and using CNG-compatible TSI and hybrid technologies.
Škoda Auto: Recent Main Electric Vehicle Models / Technology Concepts
Vision X Concept
・Urban crossover AWD hybrid concept. It was unveiled at the Geneva auto show in 2018. ・Equipped with CNG-compatible inline 4 1.5 TSI G-TEC engine. The engine’s maximum output is 96kW (130hp) and maximum torque is 250Nm. ・Equipped with a CNG tank under the rear seat and behind the rear axle. ・A 48V battery under the center floor drives the belt-type starter generator (BSG) which is attached to the engine and the rear motor. There is no cardan shaft between the front and rear, contributing to weight reduction. The motor’s function is to assist when needed. The vehicle can travel 2km driven only by the motor. There is also an energy regeneration function. ・CO2 emission is 89g / km. Cruising range is up to 650km. ・The small SUV Kamiq based on the Vision X design will be mass-produced in China and Europe from 2018–2019.AWD Hybrid with CNG Engine + BSG + Rear Motor

Vision iV Concept
・MEB-based crossover BEV concept. It was unveiled at the Geneva auto show in 2019. This concept is closer to mass production than the Vision E announced at the Frankfurt auto show in 2017.. ・AWD BEV with front and rear motors. System output is 225kW (306PS). Maximum speed is 180km / h. ・Water-cooled lithium-ion batteries are installed under the floor between the front and rear axles. Battery capacity is 83kWh. Delivers 80 percent charge in 30 minutes. Electronically-controlled electric flow between the two motors and the batteries. ・Cruising range of up to 500km (WLTP). ・A production model based on the Vision iV is scheduled to go into production at the Mladá Boleslav plant in 2020.Citigo iV
BEV version of the A segment car Citigo. Mass-production model was released in May 2019. ・It shares the same system with the VW e-up. Motor output is 61kWh. A 60Ah lithium-ion battery (168 cells) is installed in the center under the floor. Battery capacity is 36.8kWh. Cruising range is 265km (WLTP). CCS and 40kW DC connection can be charged for 80% in 1 hour by rapid charging. With 40kW DC connection (CCS cable), the vehicle can be charged 80 percent in one hour.Citigo BEV System


